What is JSON?
What is JSON?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a type of notation used for expressing structured data. BLOCKS uses data expressed in JSON in many situations.
This document is intended for those unfamiliar with JSON and only covers the basics required for using JSON in BLOCKS. For a more detailed explanation, please refer to Introducing JSON open_in_new and RFC 7159 open_in_new .
Example JSON data
Consider the profile information shown below:
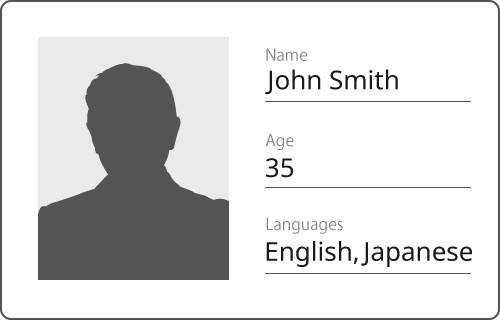
The following is an example of expressing that information in JSON:
{"name":"John Smith","age":35,"languages":["English","Japanese"]}
You can also use line breaks and spaces to make JSON easier to read.
{
"name": "John Smith",
"age": 35,
"languages": ["English", "Japanese"]
}
Both examples express the same data.
In JSON, you write data as a collection of “name” and “value” pairs. For our profile example, the pair "age": 35 has the name "age" and the value 35.
We refer to data expressed in JSON as JSON text.
Writing JSON
The types of data (values) that can be expressed using JSON are as follows: strings, numbers, arrays, objects, and literal names (true, false, null).
| Value type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| String | Characters contained within a set of double quotation marks ("). Example: "John Smith" |
| Number | Numbers represented in base 10. Scientific notation can also be used. Examples: 35, 1.234e-5 |
| Array | Multiple values separated by commas (,) and contained within square brackets ([ and ]) Each value within an array is called an element. Example: ["English", "Japanese"] |
| Object |
Multiple name and value pairs.
|
| true | Boolean true. true must be written in all lower-case characters. |
| false | Boolean false. false must be written in all lower-case characters. |
| null | Expresses that the value is empty. null must be written in all lower-case characters. |
In JSON, these values are combined to express data as shown in Example JSON data.

